
What is DKIM and How to Set up DKIM Record on Your DNS Settings
What if we said your emails wouldn’t be seen by your recipients at all, no matter how perfect they are?
Isn’t that shocking?
The reality is, that it’s happening regularly. You might have designed a perfect email with all the best practices and felt like your job is done. But it might never reach its destination. Or even worse, land in that spam folder.
But why?
This is because, your email servers use security measures to protect against malicious content, and the extra layer of security that can ensure your emails are trusted is DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail).
In this article, we will explain DKIM, why you need it, and how to set up DKIM records so you can ensure the deliverability of your emails by yourself.
Let’s start.
What is DKIM?
DKIM, or DomainKeys Identified Mail, is an email authentication method that helps protect senders and recipients from spam, spoofing, and phishing. It works by adding a digital signature to the email’s header, which can be verified by the recipient’s mail server using a public key published in the sender’s DNS records.
This process ensures that the email hasn’t been modified during transit and confirms that it was sent from an authorized domain. This is like using a special wax to seal your letters with your unique stamp so your friend knows the letter is really from you and hasn’t been tampered with.
In the digital mail system, DKIM works similarly:
- Digital Signature (Wax Seal): When you send an email, DKIM adds a digital signature to the email’s header, like sealing a letter with your unique stamp.
- Public Key (Recognizable Seal): The public key, published in your DNS records acts like the recognizable seal. The recipient’s mail server uses this key to verify the digital signature.
- Verification (Trust): If the signature matches, the recipient’s mail server confirms that the email is authentic and it hasn’t been tampered with, just like your friend trusts the sealed letter.
Once the receiver determines that an email is signed with a valid DKIM signature, it can be confirmed that the email’s content has not been modified. In most cases, DKIM signatures are not visible to end-users, the validation is done on a server level.
If DKIM is used together with DMARC or SPF, you can protect your domain against the scammers who pretend to be you.
What is a DKIM Record?
A DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) record is a type of DNS (Domain Name System) TXT record that stores the public key used for verifying the digital signature of an email. This record is essential for the DKIM authentication process, which helps to ensure that an email has not been altered during transit and that it truly comes from the original domain.
The Components of a DKIM Record
A DKIM record typically includes the following components:
- v=DKIM1: Indicates the version of DKIM being used
- k=rsa: Specifies the key type, usually RSA
- p=public_key: Contains the public key used to verify the email’s digital signature
Example of a DKIM Record
Here’s what a DKIM record might look like in a DNS TXT record:
default._domainkey.example.com IN TXT "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQDlK9..."- default: The selector, which allows multiple DKIM keys to be used for the same domain.
- _domainkey: A fixed part of the DKIM record name.
- example.com: The domain name.
Why Should You Use DKIM?
Implementing DKIM comes with a range of advantages, primarily focusing on email security and improving deliverability. Here’s how DKIM can benefit you:
- Prevents Email Spoofing: DKIM stops attackers from sending fake emails that look like they come from a trusted source
- Enhances Email Deliverability: DKIM improves email deliverability because the emails that are DKIM-signed have lower chances of being marked as Spam, which ensures your email will land up in the right inbox
- Protects Against Phishing and Spam: By ensuring the authenticity of the sender, DKIM helps to protect your recipients from phishing attacks and spam emails
- Improves Brand Reputation: It can improve the reputation of your domain which positively affects deliverability and trust
Overall, if you apply DKIM record in your email authentication method it will be beneficial both for you and your audience.
How DKIM Works?
DKIM might feel a bit complicated if you are a non-techy. Don’t worry, we will explain you in the simplest way possible so you can easily learn how it works.
As we said earlier, the DKIM signature exactly acts as a “digital stamp,” which seals the email to prove that it came from the sender and that it hasn’t been altered in transit.
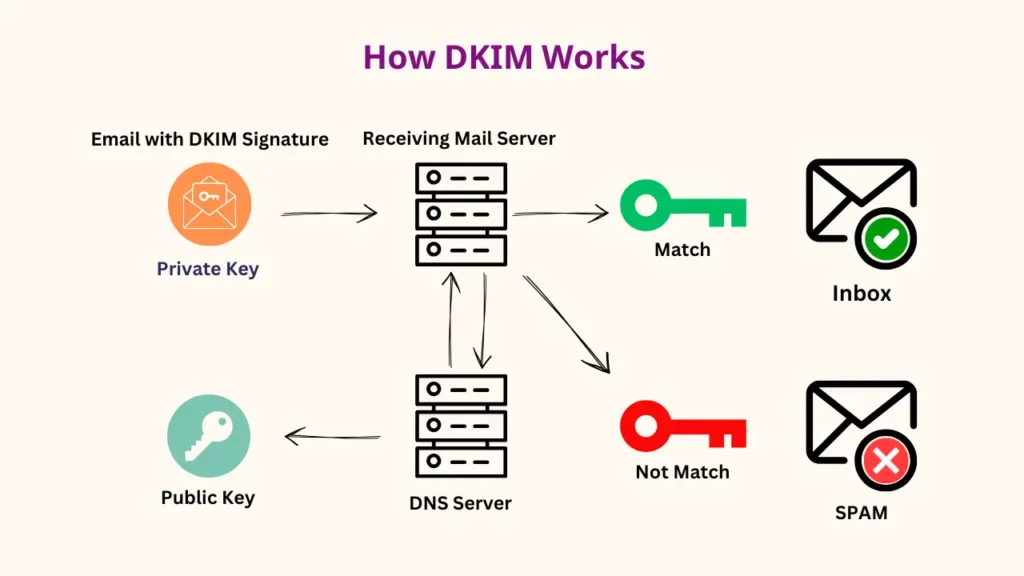
So, basically, the process starts from the sender that’s you actually. That’s why when you are sending an email your email-sending domain generates two keys;
- Private key: kept secret and used to generate digital signature
- Public key: Published in the DNS records of the sender’s domain
When an email is sent, the mail server uses the private key to generate a digital signature for specific parts of the email (subject, body, pre-header, etc.). The signature is added as a new email header field called DKIM-Signature.
The DKIM signature included a “ hash” value and Information about the signing domain and public key location in DNS. As a result, if someone alters your email, email authentication will fail.
Now it’s time to publish the public key. The sender’s domain publishes the public key as a TXT record in its DNS record. The DKIM TXT record will look like this:
selector._domainkey.example.com TXT "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=PUBLIC_KEY_HERE"Once the receiving server finds your sending email, the first thing it will do is check your email header for the presence of a DKIM signature. The server then looks up the corresponding public key in the domain’s DNS records by using the domain and selector information from the signature.
It then decrypts the signature with the public key and compares it with the private key which results in the hash it computes from the actual content of the email. If the two keys are matched, it confirms the validity of the email and the sender.
That means it has not been modified during its transmission. On the other side, if the signature doesn’t match, the email may be recognized as suspicious or rejected.
How to Setup DKIM Record?
Every hosting provider gives DNS access to their users so that you can easily add a DKIM record to your DNS record. We know there are a lot of email service providers people use. But for all the service providers the configurations are almost the same. This time, we will show you an easy DKIM configuration with the most common email service provider: Google Workspace
Here’s a step-by-step setup:
Generate DKIM Keys
- Sign in to your Google Admin console.
- Go to Apps > Google Workspace > Gmail > Authenticate email.
- Select the domain you want to authenticate and click Generate new record.
- Choose a DKIM key bit length (2048-bit is recommended) and click Generate.
Publish the Public Key in DNS
- After generating the key, Google will provide a TXT record value.
- Go to your domain’s DNS settings (this could be with your domain registrar or DNS hosting provider).
Add a new TXT record with the following details:
- Name/Host/Alias: google._domainkey.yourdomain.com (replace yourdomain.com with your actual domain).
- Type: TXT
- TTL: 3600 (or your preferred TTL)
- Value: The TXT record value provided by Google.
Configure Your Email Server
- In the Google Admin console, go back to Authenticate email.
- Click Start authentication next to the domain you set up the DNS record for.
Enable DKIM Signing
- Ensure that DKIM signing is enabled by checking the status in the Google Admin console. It should show as “Authenticating email”.
Verify DKIM Setup
Send an email from your domain to a service like DKIMValidator to check if the DKIM signature is present and valid.
In this setup process, we use Google Workspace but for detailed instructions specific to your email service provider, you can refer to their documentation. For example, Microsoft 365 has a comprehensive guide on setting up DKIM.
Also, you can follow some best practices of email security to add extra security of emails to improve better deliverability and safety of your emails.
Enhance Your Email Security with DKIM!
Setting up a DKIM record is an essential step to improving your email security and ensuring the authenticity of your emails. You can prevent email spoofing and improve your email deliverability by following the steps for setting up a DKIM record outlined in this article.
In summary, you need to generate your DKIM keys, attach the public key to your DNS records, and configure your email server to sign the messages going out. This will ensure that your DKIM settings are regularly monitored and updated, retaining integrity in your email communications. You can be more confident and assured that with DKIM in place, your emails reach securely to their intended recipients.

Ratul Ripon
I enjoy turning complex ideas into simple ones and engage with people through my writing. With a background in Oceanography, I create technical content that’s both easy to understand and interesting.
Table of Content
Subscribe To Get
WordPress Guides, Tips, and Tutorials












Leave a Reply