
POP3 vs IMAP: Key Differences You Should Know to Choose the Right Email Protocol for You
Ever felt frustrated when your email doesn’t show up on all your devices, or worse, disappears when you’re offline?
You might be using the wrong email protocol!
Whether you manage work on multiple devices or need access to messages on the go, choosing between POP3 and IMAP can make all the difference.
IMAP and POP3 are two protocols that allow you to download email from a remote server to your local email client.
But a serious question might be floating in your mind: which protocol should you use?
Don’t worry, in this guide, we’ll break down the key differences between the two protocols and help you choose the one that simplifies your email management and keeps you connected wherever you are.
Let’s dive in.
What is POP/POP3?
POP, or Post Office Protocol, is one of the oldest email protocols used for retrieving emails from a email server. The most common version is POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3).
With POP3, emails are downloaded from the server to a single device and usually deleted from the server afterward, making it suitable if you want to access your emails offline or prefer to store them on your local device.
How POP3 Works?
When you configure your email client with POP3, it connects to your mail server and downloads all new emails to your device. By default, these emails are removed from the server once they’ve been downloaded.
Also, POP3 is a one-way communication protocol, meaning that after the download, the server doesn’t keep a copy of your emails unless you configure it otherwise.
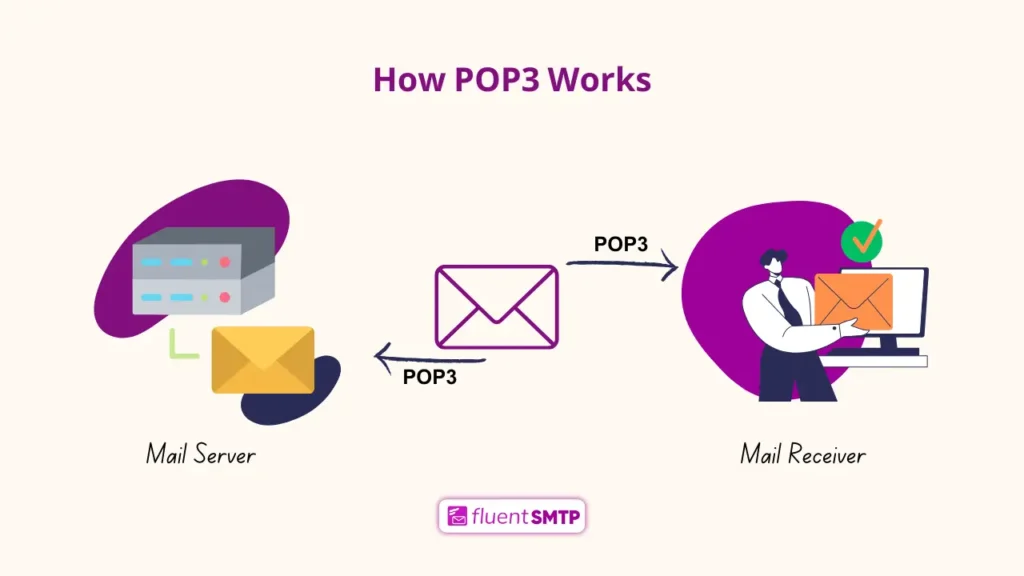
For example, using POP3 is like picking up your email from the post office (server) and taking it home (your device). Once you have the mail, the post office deletes its copy. So, you can only read the mail at home, and if you lose it, it’s gone for good unless you set it to keep a backup at the post office.
What are the Pros and Cons of POP3?
While POP3 makes email access more convenient in some ways, it also introduces limitations that can affect how you manage and interact with your messages.
Pros:
- Offline access: Emails are stored on your device, so you can read them without an internet connection
- Storage control: Emails don’t take up space on the server, which is helpful if you have limited server storage
- Simplicity: Easy to set up and use, making it beginner-friendly
Cons:
- Limited device access: You can only access your emails on the device where they were downloaded
- Data loss risk: If your device is lost or damaged, you could lose your emails unless they are backed up
- No email sync: Changes like marking emails as read or deleting them won’t show up on other devices or the server
What is IMAP?
IMAP, or Internet Message Access Protocol, allows you to access your email from multiple devices. When you read an email using IMAP, you aren’t actually downloading or storing it on your computer; instead, you’re reading it from the email service. This means you can check your email from different devices, anywhere in the world.
Unlike POP3, with IMAP, emails are stored on the mail server and synced on all devices. This means when you read, move, or delete an email, those changes are reflected on all your devices.
How Does IMAP Work?
When you connect to the server via IMAP, it synchronizes your emails, keeping a copy on both the server and your devices. You interact with emails on the server directly rather than downloading them for offline use (though you can download copies for offline access).
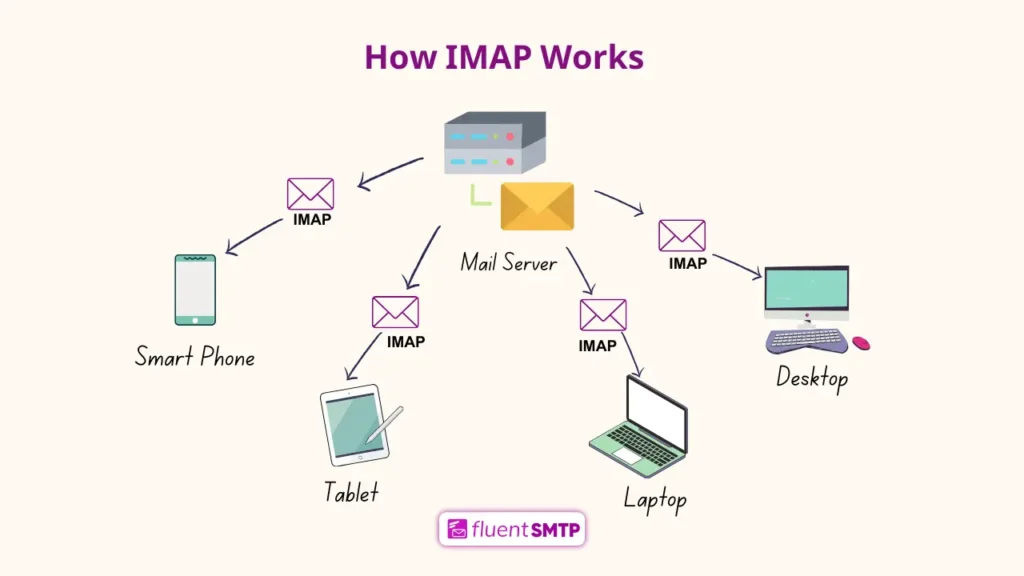
IMAP is like keeping your mail at the post office but checking it from any location (any device). If you read or organize your mail, those changes are seen everywhere. The mail stays at the post office, but you can still download a copy if you need it.
What are the Pros and Cons of IMAP?
IMAP is widely used for its flexibility, but like any protocol, it has its strengths and drawbacks.
Pros:
- Access from multiple devices: IMAP allows you to access and manage your email from any device.
- Server-side sync: Actions like marking emails as read or moving them to folders are synced on all devices.
- No data loss: Emails are stored on the server, so you can still access your emails even if a device is lost.
Cons:
- Internet required: Since emails are stored on the server, you need an internet connection to access them (although some clients support offline access)
- Server storage limits: Since emails remain on the server, they can take up a lot of space if not managed properly, potentially leading to storage limits
- Complexity: IMAP can be more complex to set up and manage, especially when dealing with large email accounts
Note: While POP3 and IMAP responsible for receiving emails, SMTP is the protocol is responsible for sending emails. Typically, SMTP uses SMTP port numbers 25, 465, or 587 for this process.
Key Differences between POP3 and IMAP
Choosing between POP3 and IMAP affects how you manage your emails. Whether you prefer local storage or syncing on multiple devices, this table highlights the key differences to help you decide.
| Features | POP3 | IMAP |
| Storage | Downloads emails to a single device and deletes them from the server. Suitable for local storage with limited server space | Emails are stored on the server and accessible from multiple devices, preserving server space |
| Synchronization | There is no synchronization between devices. Once downloaded, changes made on one device won’t reflect elsewhere | Full synchronization in multiple devices. Any action (read, delete, move) is reflected on all connected devices |
| Access | Emails are accessible offline after download | Requires an internet connection for full access, but headers can be accessed offline |
| Organization | Email organization is limited to the local device | Allows for the server-side organization (folders, labels) that are synced to each other |
| Backup & Recovery | If emails are deleted from your device, they’re gone unless backed up manually | Emails are stored on the server, so you can recover them even if something happens to your device |
| Security | Encrypted over port 995 (SSL/TLS), which secures email transfers | Encrypted over port 993 (SSL/TLS), offering secure email transfers |
| Use Case | Perfect for users who have limited internet access or prefer offline access to all their emails | Ideal for users who need access from multiple devices—professionals or travelers |
POP3 vs IMAP: Which One is Better?
IMAP4 and POP3 serve different email management needs, and choosing between them depends on your preferences.
IMAP4 is ideal for users who need to access and sync emails through multiple devices, while POP3 is best for those who prefer to manage emails on a single device, here’s when you might prefer one over the other:
Go with POP3 If,
- You prefer downloading emails to one device and accessing them offline without needing an internet connection
- Limited server space is a concern, and you’d rather keep emails stored locally
- You’re okay with managing emails on just one device, like your primary computer or phone
- You often work in places with poor or no internet, making offline access a top priority
Choose IMAP If,
- You need to access your emails through multiple devices—like a phone, laptop, and tablet
- You want email organization (folders, labels) to stay synced on all devices
- You like the security of having your emails backed up on the server, making recovery easy if needed
- You want any changes—reading, deleting, or moving emails—to sync on all devices automatically
Ultimately, your specific needs determine which protocol you should use.
Why POP3 and IMAP Matters for WordPress Users?
As the FluentSMTP team, we know how critical email management is for WordPress users. Whether you’re sending transactional emails, newsletters, or managing customer inquiries, choosing the right protocol can make all the difference.
Why?
Your customers and B2B contacts may be sending you a wide variety of emails including sales query, support requests, partnership proposals, etc.
These communications are vital and requires your entire team in some cases. And that’s why we’ve set up our receiving email client with IMAP to ensure we never miss a customer’s email or query. Most modern email clients also provide better support for IMAP—making things more efficient.
With everything synced between devices, our team can respond quickly and stay on top of customer interactions, no matter where we are. We also enjoy enhanced data security, as emails are stored on the server, minimizing the risk of data loss and helping us maintain security while working remotely, while ensuring accessibility for team members in different locations.
However, POP3 can be a good option for solo entrepreneurs who primarily manage emails on a single device and need offline access. POP3 downloads emails to one device and frees up server space, but it lacks the synchronization that IMAP provides.
While it may suit individuals with limited internet access, for teams working on single devices, IMAP offers greater flexibility and control.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, both POP3 and IMAP serve important roles in managing your emails, but the best choice depends on your needs. If you prefer storing emails on one device and accessing them offline, POP3 might be ideal.
On the other hand, if you require flexibility, syncing across multiple devices, and organizing emails on the server, IMAP is the better option.
By understanding the differences, you can choose the protocol that best suits your email habits, ensuring a smoother and more efficient email experience.
Best of luck!
FAQs

Ratul Ripon
I enjoy turning complex ideas into simple ones and engage with people through my writing. With a background in Oceanography, I create technical content that’s both easy to understand and interesting.
Table of Content
Subscribe To Get
WordPress Guides, Tips, and Tutorials












Leave a Reply